What is DAS?
A Distributed Antenna System (DAS) is a network of antennas strategically placed to enhance wireless coverage within a specific area. The primary purpose of a DAS is to improve the quality and reliability of wireless communication, especially in large or challenging environments such as stadiums, airports, hospitals, campuses, and urban areas.
The two most common types of DAS systems are described below.
Passive System
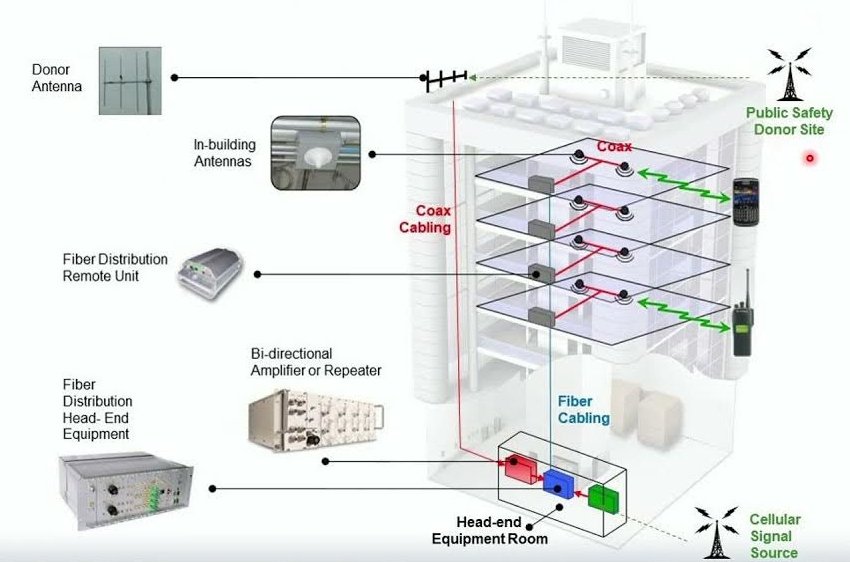
A passive DAS is typically an open air repeater using coaxial cable only. The passive system uses one or more donor antennas that will communicate with the closest cell towers or base station. The donor antennas connect directly to a repeater or series of repeaters and then the signal is sent from the repeater to a server antenna or series of server antennas. These systems are generally used for smaller coverage area footprints below 250,000 square feet. Examples of where we install these systems are small and large homes, small offices or home offices (SOHO), boats and even cars. They can be either single carrier or multiple carrier systems. These systems are much more cost effective, quick to deploy and easy to install. All of these systems need to carrier and FCC approved.*
Active System
The active system is different from passive because it uses a fiber optic cable distribution system as well as a different signal source such as a base transceiver station (BTS) or small cell application. These systems are much more complex and require expert RF engineering. Using this system requires a fiber head end that will convert the radio frequency (RF) to light which then sends the light to a remote or series of remotes that then covert the light back to radio frequency (RF) and then distributes to a series of server antennas. These systems are used in large coverage areas above 250,000 square feet such as stadiums, high rise buildings, hospitals, casinos, hotels, etc. These systems can be designed for large public safety applications, single carrier use or neutral host, meaning a shared system with one or more carriers.
Request a Free Quote
Public Safety DAS
A Public Safety Distributed Antenna System (DAS) is a system designed to improve communication for emergency services and first responders, particularly in buildings or areas where radio and wireless communication signals may be weak or non-existent.
Public Safety DAS are required to meet certain criteria outlined in the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) and International Fire Code (IFC) standards. These standards are intended to ensure that emergency personnel can effectively communicate with one another and their command centers during a crisis.
Much like a Cellular DAS, a Public Safety DAS consists of a network of antennas distributed throughout a building or area to enhance signal strength and reliability. However, instead of enhancing commercial cellular signals, they enhance radio frequencies used by emergency services such as police, fire, and ambulance services.
The critical features of Public Safety DAS include:
Support for specific frequencies: These systems are designed to support the specific radio frequencies used by public safety agencies. These frequencies can differ depending on the location and the agencies involved.
24/7 monitoring: Public safety DAS are required to include supervisory alarm monitoring to ensure that the system is always functional and to alert the necessary parties if a part of the system fails.
Battery backup: In order to ensure functionality during power outages, these systems need to have a substantial battery backup.
Signal strength: The system should be capable of providing a certain level of signal strength throughout the building or area, including in hard-to-reach places like stairwells and underground areas.
Public Safety DAS are used in a wide range of settings, including high-rise buildings, schools, hospitals, stadiums, tunnels, and more. They are critical in ensuring effective communication for first responders during emergencies.
Cellular DAS
A Cellular Distributed Antenna System (DAS) is a network of spatially separated antenna nodes connected to a common source through a transport medium that provides wireless service within a geographic area or structure.
The purpose of a DAS is to enhance the quality of cellular signals in areas where reception would typically be poor, such as inside large buildings, underground facilities, or densely populated areas. A DAS network can be used to support multiple wireless carriers, technologies (like 4G, LTE, 5G), and frequencies simultaneously.
The system is made up of two primary components:
Antenna nodes: These are spread throughout the area where coverage is needed and are responsible for transmitting and receiving cellular signals.
Central hub: This component processes and distributes the cellular signals to and from the antenna nodes.
In the case of an indoor DAS, the system works by receiving signals from a cell tower, amplifying them, and then distributing them to antenna nodes located throughout the building. This enhances the quality and strength of the cellular signals, ensuring that users within the building have strong, reliable coverage.
DAS networks can be a very effective solution to overcome the problem of poor cellular coverage in difficult areas, and they are used in a wide range of settings, including hospitals, office buildings, shopping malls, stadiums, and more.